第九届“强网杯”全国网络安全挑战赛
Misc
谍影重重 6.0
Challenge
经过我国执法部门的努力,终于在今年十月提取出了张纪星(系杜撰名字,与现实人员无关)被捕前布置的监听设备中的加密信息,据本人供述其曾恢复过我国一份绝密情报。
flag为情报所提及的详细时间和地址的md5值,即flag{md5(x年x月x日x时x分于x地)}。
题目提示:本题依托于架空的时间线,取材自真实历史事件,请关注地点信息。
Solution

先看看协议分级,发现全是 UDP 流量

先查看第一个包的 payload,发现是以 80 开头的,这使我不禁想起前段时间的 WMCTF2025,参考当时写的 wp:Voice-hacker
先假设它是 RTP 流量,然后用同样的方法解析它的头部 80 80 76 38 99 59 48 23 88 48 19 ee:
- 80: 版本号(V=2)
- 80: 标记位(M=1),载荷类型 (Payload Type, PT) = 0
- 76 38: 序列号 (Sequence Number) = 30264
- 99 59 48 23: 时间戳 (Timestamp) = 2572765219
- 88 48 19 ee: 同步源标识符 (SSRC) = 0x884819EE
完美对上了,这就是 RTP 协议,右键第一条流量在 Decode As... 把端口 40000 的 UDP 流量解析为 RTP
然后往下滑,发现还有多个端口,把端口 40001 的也解析了

不难发现,这个流量文件里并不是所有包的 SSRC 都相同的,这就意味着并不是所有包都属于同一个音频流,需要根据 SSRC 来划分
先用 tshark 把 UDP 包的 Payload 提取出来方便稍后使用脚本处理:
1 | tshark -r Data.pcap -T fields -e data > Data.txt |
由于里面的流量并非全部属于同一个音频流,因此需要根据 SSRC 划出多段音频,最后将它们按顺序拼接起来合并成同一个音频文件,这里在 Voice-hacker 的脚本的基础上进行修改。
这样简单的处理得到的结果效果并不好,出现了两个问题:音频的音量过小,音频长达 18 小时😰
在听了两三分钟后,发现音频中存在较长的空白片段,随便往后一划也很容易划到没有声音的地方,检查一下前面导出的 Data.txt ,可以发现:
1 | 8000c6445d9424d7842e8e8fffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffff |
里面存在大量类似这样的片段,因此我们可以先做一个预处理,修改 Data.txt,删除里面所有完全空白的片段:
1 | kept_lines_count = 0 |
Data.txt 从原来的 1.04 GB 缩小成了 195 MB(看来掺水挺严重
下面是完善后的导出脚本:
1 | import wave |
用语音识别模型(我用的是 FunASR)识别导出的 combined_audio.wav 得到字幕文件
粗略看了下没啥信息,是由多条听起来有点逻辑的语句直接拼接起来的,然而实际上并没有任何意义
因为附件还给了个 Secret.7z 压缩包,联系到题目描述不难想到“监听设备中的加密信息”指的是这些录音,那么“绝密情报”就是 Secret.7z 了,进而可以推测音频中隐藏着 Secret.7z 的解压密码
看了下字幕文件只有 14207 行,索性直接一股脑丢给 Gemini 问问看有没有比较突兀的地方

回到字幕文件找到这一段

定位到这个片段发现确实是在念数字,人工识别得到:
1 | 651466314514271616614214660701456661601411451426071146666014214371656514214470 |
尝试使用这串数字作为密码解压缩包失败了,观察发现字符的范围是 0-7,因此推测这里要八进制转字符
用动态规划算法切成若干个长度为 2 或 3 的八进制段寻找可能的解:
1 | s = "651466314514271616614214660701456661601411451426071146666014214371656514214470" |
发现有且仅有一个解:5f3eb916bf08e610aeb09f60bc955bd8
这个解就是压缩包的解压密码,解开压缩包后得到 绝密录音.mp3
绝密录音.mp3 内存储了一段对话(其中A是普通话,B是粤语):
1 | A:表兄,近日可好?上回托您带的廿四旦秋茶,家母嘱咐务必在辰时正过三刻前送到,切记用金丝锦盒装妥,此处潮气重,莫让干货受了霉,若赶得及时可赶得菊花开前便可让铺子开张。 |
“廿四”指的是
24日“辰时”指的是上午 7~9时,“辰时正”指的是
8时“三刻”指的是
45分地点是对话中提到的
双鲤湖西岸南山茶铺
双鲤湖位于福建省金门,结合这些信息可以找到1949年10月24日发起的金门战役,因此年份是 1949年
连起来就是 1949年10月24日8时45分于双鲤湖西岸南山茶铺
FLAG
1 | flag{2a97dec80254cdb5c526376d0c683bdd} |
The_Interrogation_Room
Challenge
Reminder:
- Complete all rounds to get the flag (or a gift).
- Any invalid token terminates the session.
- Spaces must be added on both sides of ‘(‘ and ‘)’.
Solution
本题的核心是一个逻辑推理挑战,我们需要在25轮游戏中的每一轮都成功推断出服务器在后台生成的8个未知的布尔秘密值(S0 到 S7),挑战规则如下:
- 查询机会:每轮有 17 次提问机会
- 查询方式:提问是通过发送一个由白名单内操作符(
['==','(',')','S0','S1','S2','S3','S4','S5','S6','S7','0','1','and','or'])组成的逻辑表达式 - 核心障碍:在17个回答中,服务器会精确地说谎 2 次(即返回与真实计算结果相反的布尔值)
- 目标:利用这17个可能包含错误的回答反推出唯一正确的 8 个秘密值
这个问题本质上是一个纠错码问题,我们需要设计一个信息冗余的查询系统,使得即便信息在传输过程中出现了2个比特的错误也依然能够恢复出原始的8比特信息。
为了尽可能地提高成功率,我们要设计一个能够消除绝大多数歧义性的查询策略。
==操作符的特性:在布尔逻辑中,A == B等价于XNOR(异或非)。当链式使用时(如S0 == S1 == S2),它会检查参与运算的变量中值为True的个数是奇数还是偶数,这种校验方式比or或and提供了更强的数学约束。
因此我们可以构建一个基于奇偶校验的编码系统,使用 == 操作符来实现奇偶校验,利用全部17次查询来构建一个强大的校验矩阵。
设计查询集(17个问题)
设计如下查询组合以最大化信息获取和冗余度:
8 个直接查询:
直接查询S0,S1, …,S7。
这为我们提供了含有最多2个错误的原始数据。9 个奇偶校验查询:
设计 9 个不同的互相重叠的秘密子集并对它们进行==链式查询,这些查询充当了纠错码中的“校验位”,用于精确定位错误。1
2
3
4
5# 例如:
S0 == S1 == S2 == S3
S4 == S5 == S6 == S7
S0 == S2 == S4 == S6 # 偶数位
... (以及其他精心挑选的组合)这个查询集确保其最小汉明距离足够大,足以纠正2个比特的错误。
解码与暴力破解
在获得17个回答后采取以下步骤进行解码:
遍历所有可能性:由于秘密总共只有 8 位,所以只存在
2^8 = 256种可能的组合,可以进行暴力破解。验证每个候选解:对 256 种可能的秘密组合,执行以下验证:
a. 假设候选解为真:假设当前遍历到的组合就是囚犯心中的真实秘密。
b. 计算理想答案:基于这个假设计算出我们设计的 17 个查询的全部正确答案。
c. 比较并计算差异:将这 17 个理想答案与服务器返回的 17 个回答逐一比较,计算出它们之间有多少个不一致(即汉明距离)。
d. 寻找匹配:根据题目规则,真实的秘密组合所产生的理想答案,与服务器的回答之间的汉明距离必须精确等于2。
处理极少数的歧义情况
实验证明,存在极小概率的情况会导致找到不止一个满足条件的候选解,处理方案如下:
- 如果只找到一个解,那么它就是正确答案。
- 如果找到多个解,脚本会记录一个警告,并猜测第一个解作为答案提交。
- 如果猜测错误,服务器会断开连接。此时要重新运行脚本,重跑几次总有一次能成功通过 25 轮。
1 | from pwn import * |
1 | [x] Opening connection to 39.106.45.147 on port 39009 |
FLAG
1 | flag{42b7aa34-00c7-4c4a-88c2-c91e9ee9b315} |
Personal Vault
Challenge
My friend created a vault for each process, unfortunately we haven’t contacted for years, and this vault thing crashed my pc when I tried checking other’s secret? Please help me with this
附件下载 提取码(GAME)
Solution
非预期

FLAG
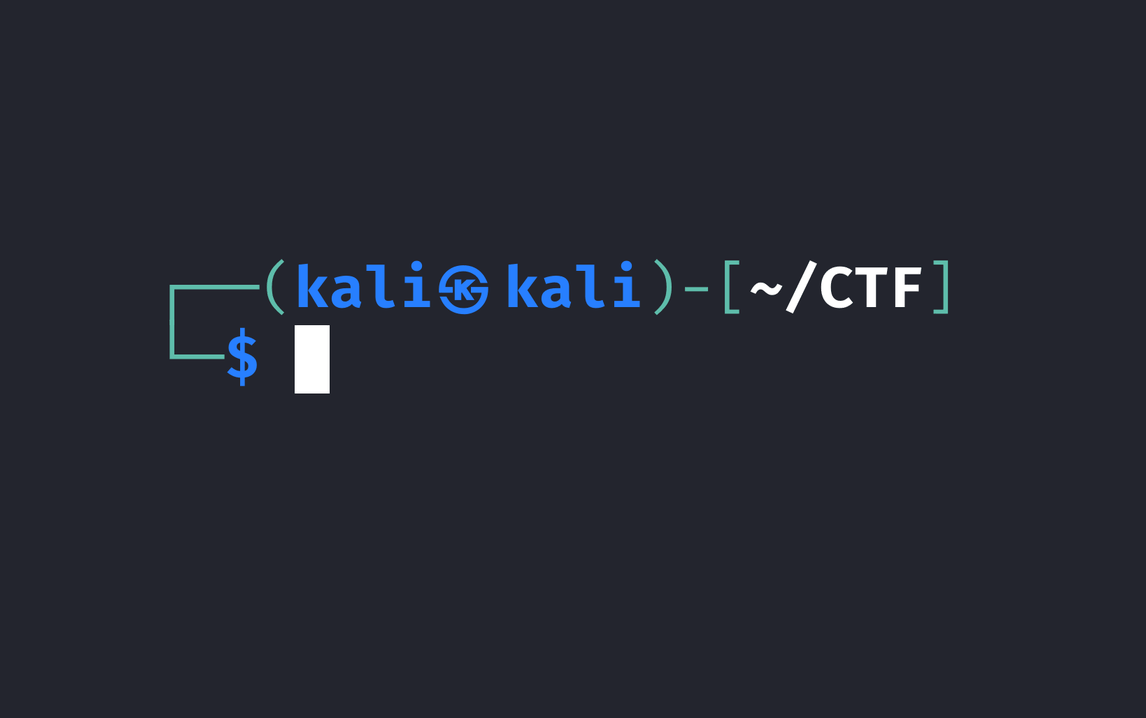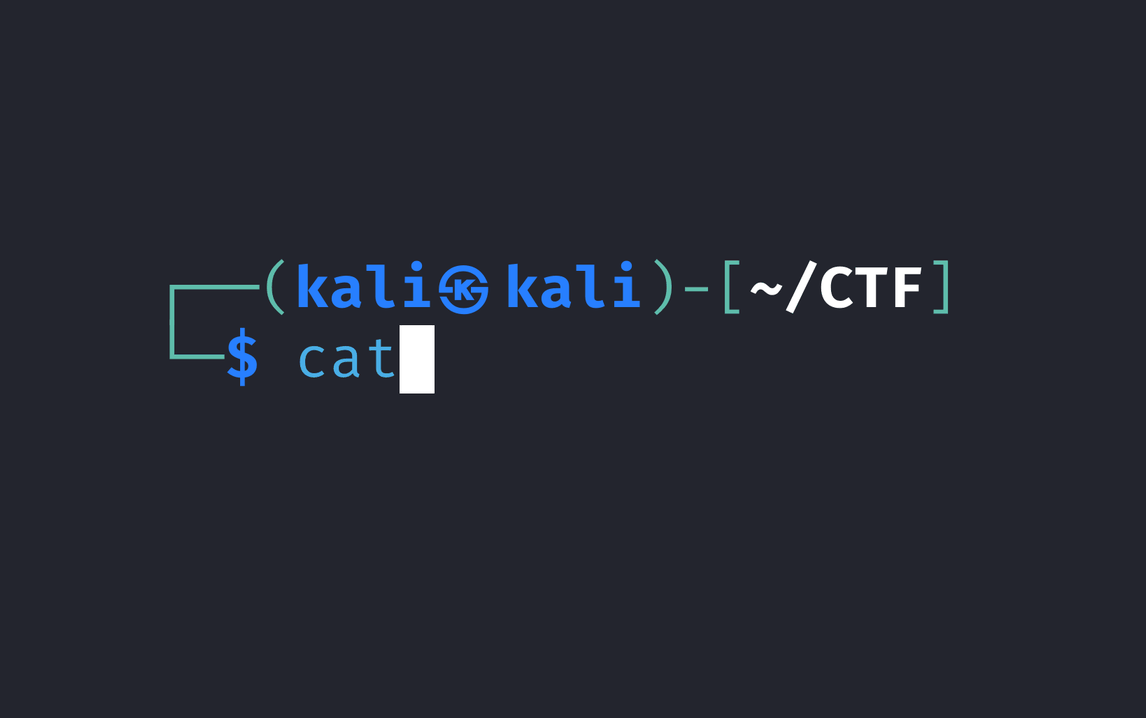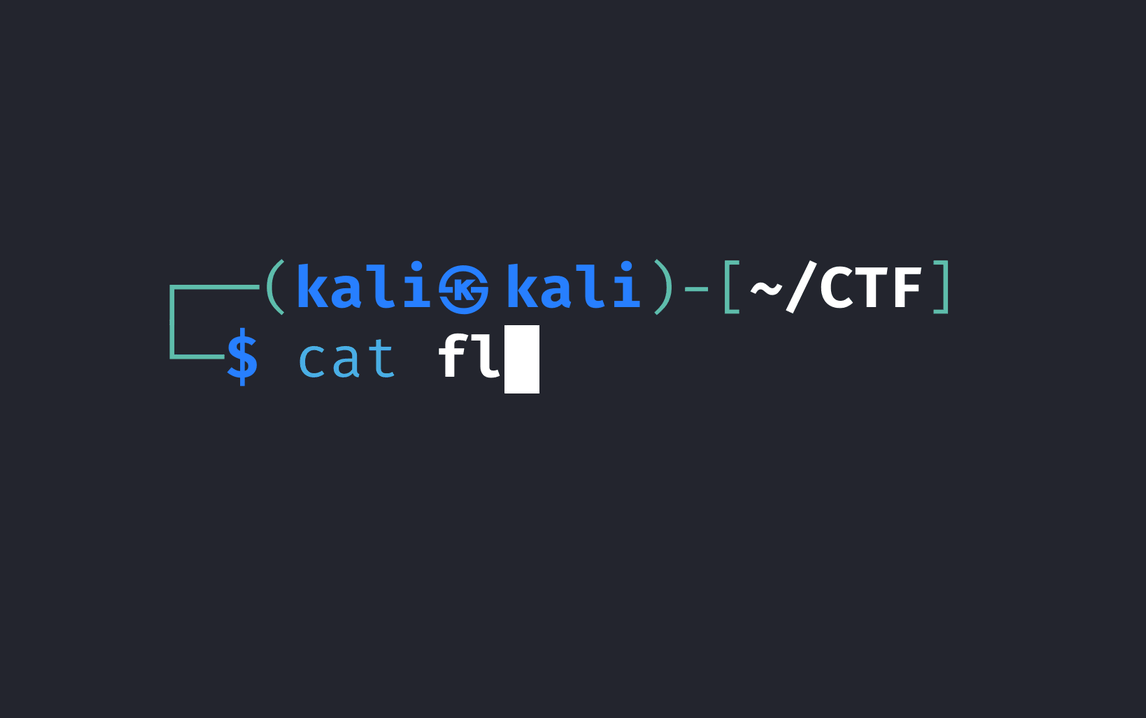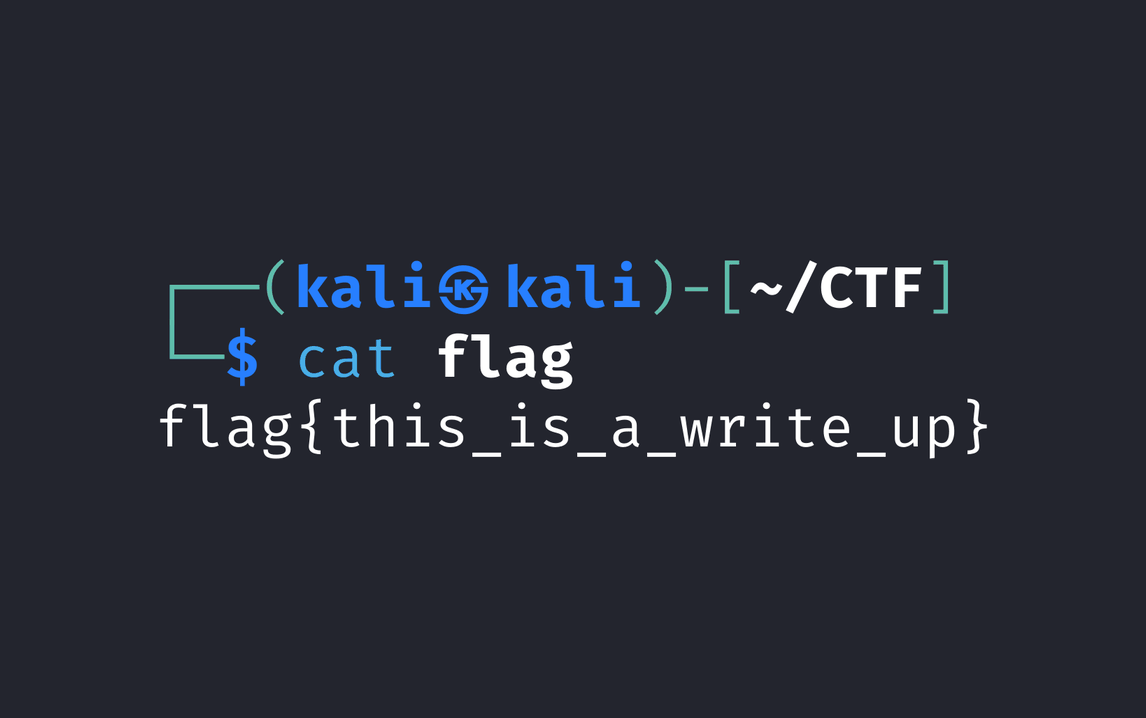
1 | flag{personal_vault_seems_a_little_volatile_innit} |
Reverse
butterfly
Challenge
(空)
Solution
入口链路与主函数定位
- 入口链路:start → __startup_libc_wrapper(0x4041B0) → cpu_feature_init_ifunc(0x403200) → call_main_trampoline(0x4021F0) → main(0x4018D0)
- 通过字符串与调用关系可见 main 打印 Usage/Encoding/Encoded size/%s.key 等信息,确认其为核心逻辑。
main@0x4018D0(核心流程)
1 | // 参数检查 |
MMX 编码循环的关键指令(0x401A49—0x401A73):
1 | movq mm0, [rax] ; 加载 8 字节数据块 |
结论(每个 8 字节块 x → y):
- y = add8( rol1( swap16( x XOR key8 ) ), key8 )
- 尾余(<8 字节)未进入 MMX 循环,保持原样。
sub_401CA0(写文件封装)
1 | int write_file(const char* path, const void* data, size_t n) { |
功能:安全写文件并校验长度;失败路径打印错误。
sub_405540(fopen 包装)
伪代码要点:
- sub_412620 分配 FILE 结构;sub_40BF90 初始化;sub_407830 做额外设置。
- sub_407E10(v3, a1, “rb”/“wb”, 1) 实际为 _IO_new_file_fopen 路径。
- 成功则返回已初始化的文件对象指针;失败则清理并返回 0。
功能:glibc _IO 层封装的 fopen-like。
sub_405640(获取长度/定位配合)
- 在互斥/线程本地存储保护下调用 sub_4057E0(a1, 0, 1, 0) 等,配合 fseek/ftell 语义。
- 返回“当前位置或大小”,与 main 的两次 sub_407480(…2/0) 配合可得文件长度。
功能:获取“文件长度”或“当前位置”的封装。
sub_407480(文件定位封装)
- 在锁保护下更新流的 owner/tid 与递归计数。
- 最终调用 sub_4057E0(a1, a2, n2, 3),n2=2/0 分别对应 SEEK_END/SEEK_SET。
功能:fseek/rewind 等价封装。
sub_41CC80(读取封装)
1 | // 溢出与区间检查 |
功能:带线程/arena 管理的 fread 等价封装(静态 glibc 影子实现)。
1 | import sys |
FLAG
1 | flag{butter_fly_mmx_encode_7778167} |
- 标题: 第九届“强网杯”全国网络安全挑战赛
- 作者: Aristore
- 链接: https://www.aristore.top/posts/qwb2025/
- 版权声明: 版权所有 © Aristore,禁止转载。